Video diffusion models (VDMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in text-to-video (T2V) generation.
Despite their success, VDMs still suffer from degraded image quality and flickering artifacts.
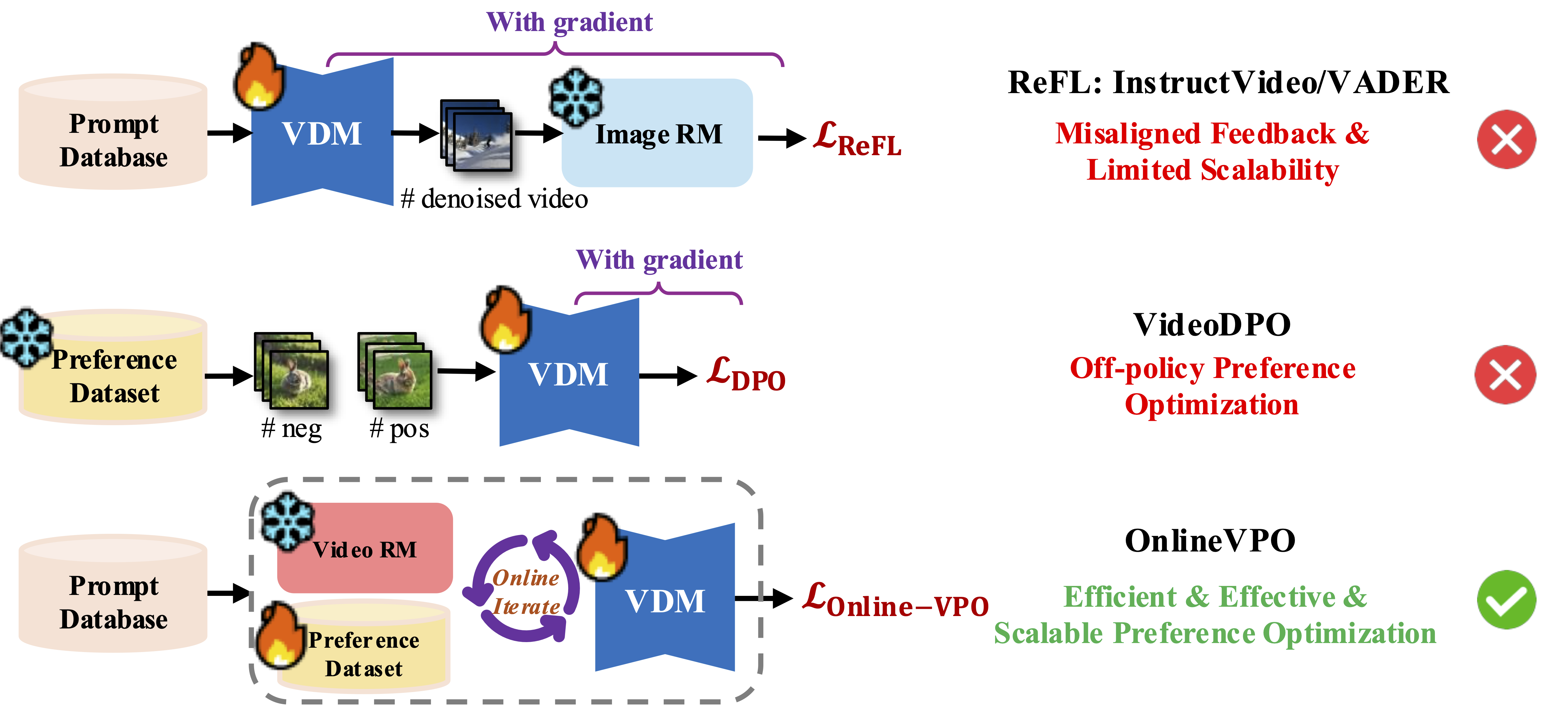
To address these issues, some approaches have introduced preference learning to exploit human feedback to enhance the video generation.
However, these methods primarily adopt the routine in the image domain without an in-depth investigation into video-specific preference optimization.
In this paper, we reexamine the design of the video preference learning from two key aspects: feedback source and feedback tuning methodology, and present OnlineVPO,
a more efficient preference learning framework tailored specifically for VDMs.
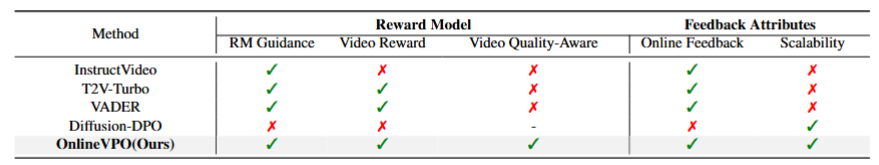
On the feedback source, we found that the image-level reward model commonly used in existing methods fails to provide a human-aligned video preference signal due to the modality gap.
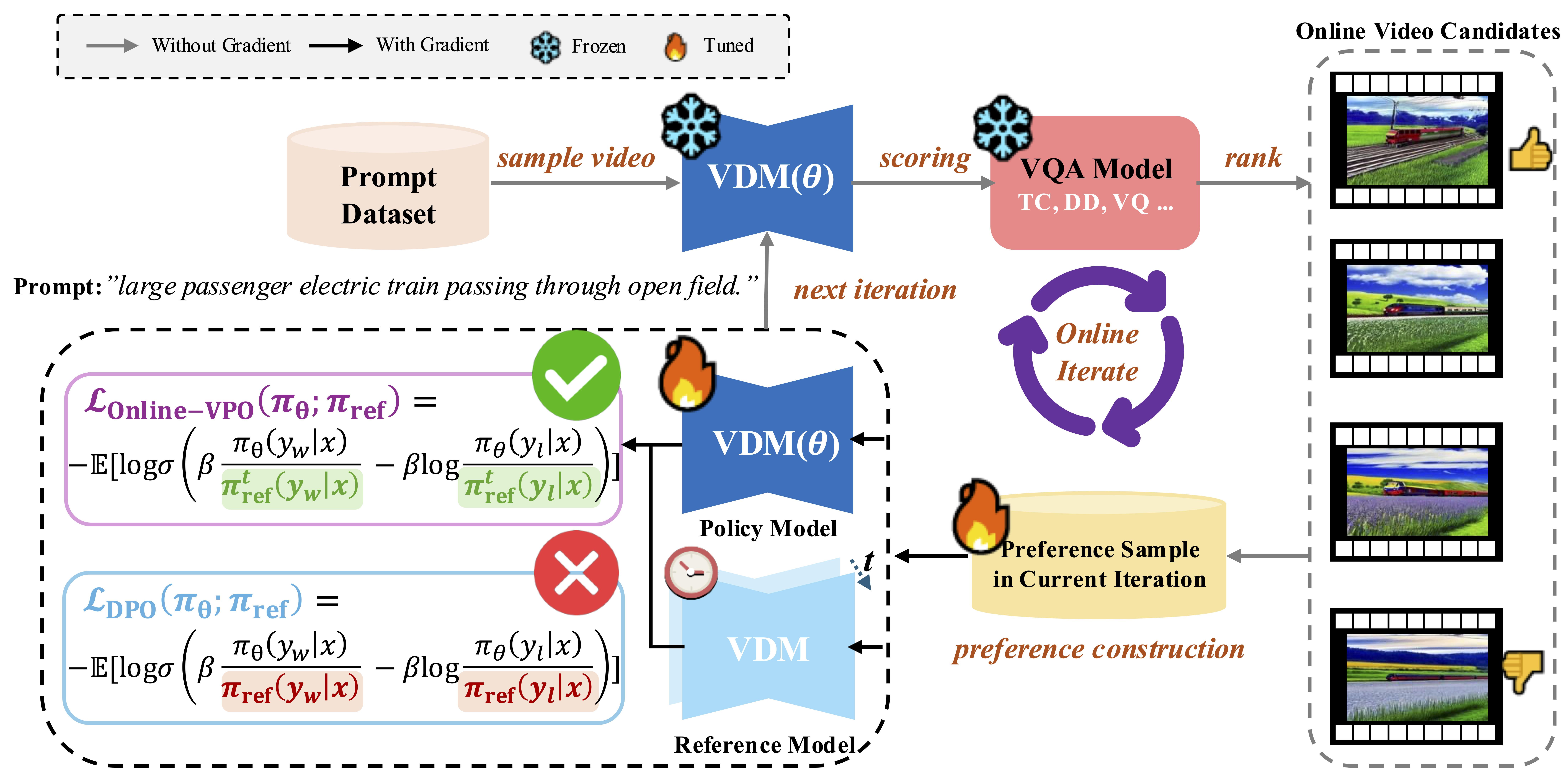
In contrast, video quality assessment (VQA) models show superior alignment with human perception of video quality. Building on this insight,
we propose leveraging VQA models as a proxy of humans to provide more modality-aligned feedback for VDMs. Regarding the preference tuning methodology,
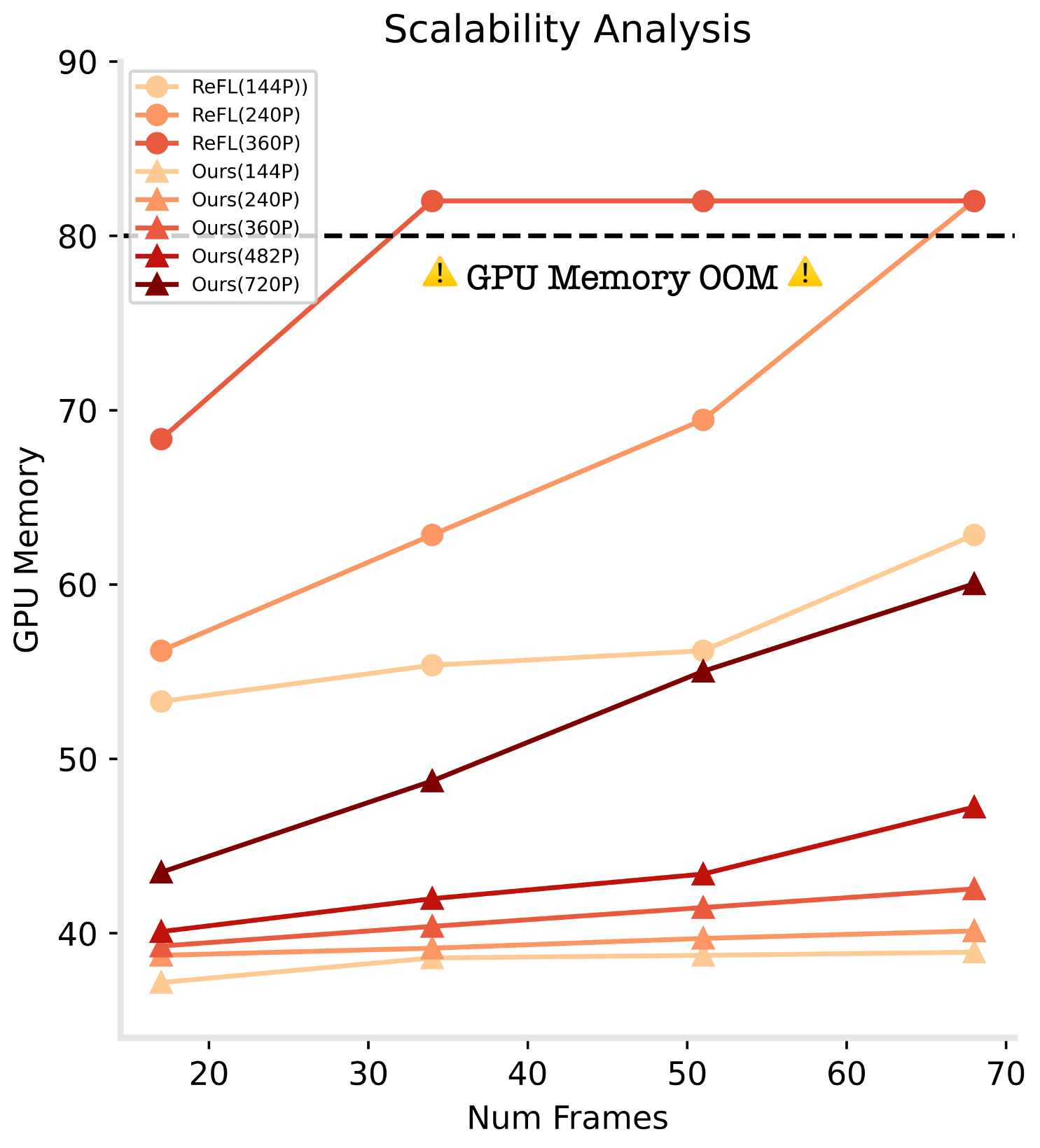
we introduce an online DPO algorithm tailored for VDMs. It not only enjoys the benefits of superior scalability in optimizing videos with higher resolution and longer duration compared with the existing method,
but also mitigates the insufficient optimization issue caused by off-policy learning via online preference generation and curriculum preference update designs.
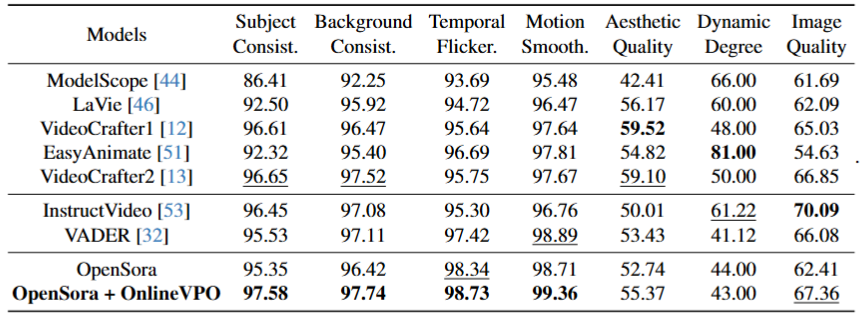
Extensive experiments on the open-source video-diffusion model demonstrate OnlineVPO as a simple yet effective and, more importantly, scalable preference learning algorithm for video diffusion models.